With 116 GW of enormous load capability dedicated or below building, U.S. utilities are planning for important giant load capability progress — equal to fifteen.5% of present U.S. peak demand — in line with a brand new Wooden Mackenzie research of main investor-owned utilities. Accounting initiatives in superior dialogue or a near-term forecast brings the overall to 147 GW, or 20% of U.S. peak demand.
The report, “No turning back, an analysis of utility large load pipelines,” exhibits a good portion of this capability will come on-line this decade, with 60 GW anticipated to be added via 2030, equal to eight% of present U.S. peak demand. Utilities anticipate 93 GW to be operational by 2035, after which little pipeline capability has been disclosed.
“Utilities are committing to giant hundreds ramping quickly this decade,” stated Ben Hertz-Shargel, international head of Grid Edge for Wooden Mackenzie. “The market shall be hard-pressed to produce this new load on that timeframe, which can forestall it from taking place.”
The report identifies a notable shift in the place giant load initiatives are sited. Whereas 91% of the present 17 GW of disclosed capability below building is situated in regulated markets, 46% of dedicated capability not but below building and 35% of capability in superior dialogue is deliberate for deregulated markets.
Almost three-quarters of high-confidence load is concentrated in ERCOT and PJM areas.
“Dedicated capability not below building in addition to superior dialogue capability fall disproportionately in deregulated markets, primarily ERCOT,” stated Hertz-Shargel. “Deregulated markets pose dangers of insufficient future provide and value will increase to non-large load prospects, which has prompted market interventions by Texas and PJM and can seemingly immediate extra sooner or later.”
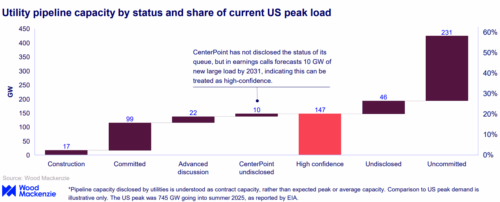 Regardless of modest will increase in high-confidence capability at a number of utilities, its share of whole pipeline capability has decreased over the previous couple of quarters as new requests outpace the development and withdrawal of present requests.
Regardless of modest will increase in high-confidence capability at a number of utilities, its share of whole pipeline capability has decreased over the previous couple of quarters as new requests outpace the development and withdrawal of present requests.
“Relatively than beginning to see a development towards pipeline certainty, we proceed to look at the other,” stated Hertz-Shargel.
Knowledge heart ramp charges are augmenting this uncertainty. The time to succeed in contract capability varies significantly for initiatives over 300 MW, typically for much longer than 4 years.
“The tempo at which utilities join information facilities is simply a part of the story,” stated Hertz-Shargel. “How quickly the grid truly sees load will in the end rely on information heart builders.”
Information merchandise from WoodMac

